
19-02-2026
Steam Turbine: Definition, How It Works, Types, & Functions
Turbines are an important component of power plants, including steam turbines, which are commonly used in steam and gas-steam power plants.
So, how do steam turbines work? This article reviews the role of steam turbines in power plants and other sectors. So, check out the following information!
What Is a Steam Turbine?
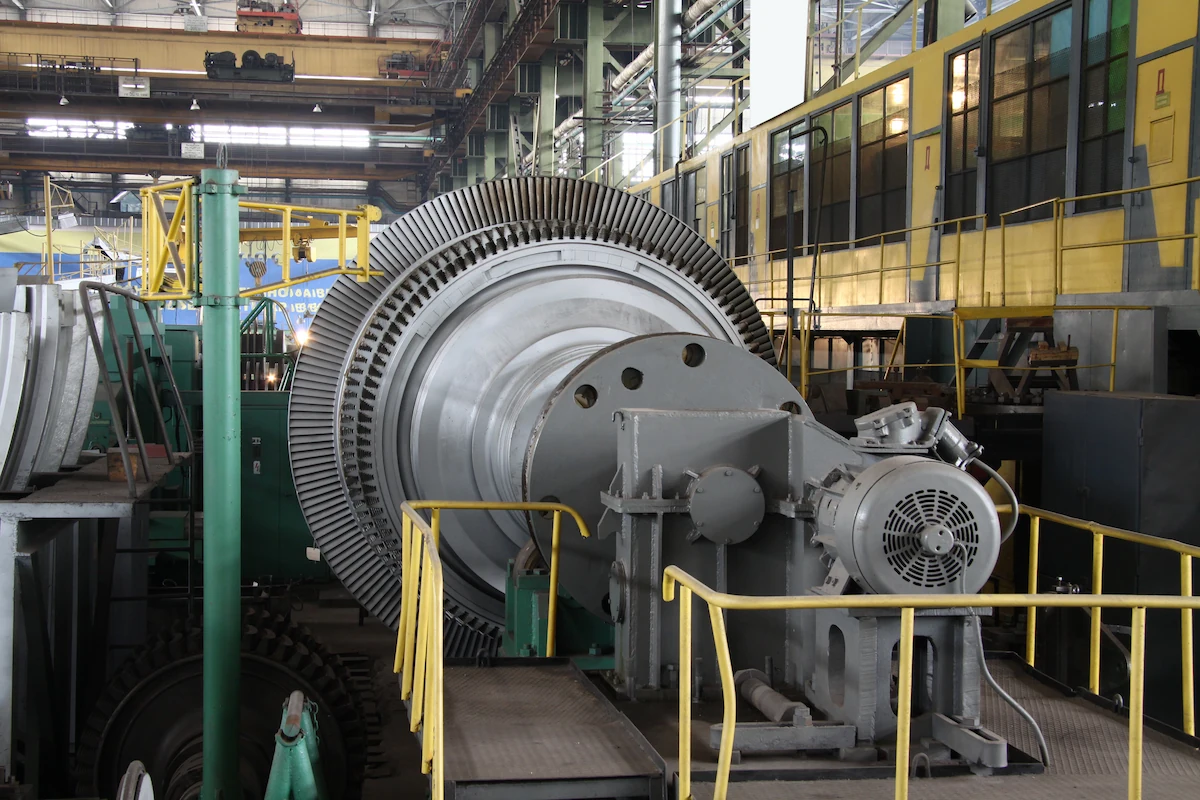

A steam turbine is a machine that can convert heat energy from steam into mechanical energy. This turbine operates according to the principles of thermodynamics, which describe the relationships among heat, work, energy, and temperature.
The steam turbine works by heating water in a boiler, which then creates hot steam. This steam is directed to the high-pressure steam turbine. Then, the steam expands rapidly as it passes through the turbine blades.
This rapid movement then rotates the turbine, generating mechanical energy. This energy turns the generator, which produces electricity.
Read also: 12 Types of Power Plants for Alternative & Renewable Energy
Steam Turbine Cycle
The initial stage of a steam turbine is the heating of water in a boiler to a very high temperature. This process produces steam that carries heat energy. This steam is directed to the condensing turbine.
When it reaches the turbine, the steam encounters the blades and rotor. As it passes through, the steam expands and cools, transferring its energy to the turbine blades.
This energy transfer process rotates the rotor, converting the steam's heat energy into mechanical energy. This process is central to the turbine's performance because it drives the generator to produce electricity.
After transferring energy, the steam enters the condenser and turns into water. The water returns to the boiler, is heated, and the cycle repeats, making the process more energy efficient.
Steam Turbine Components
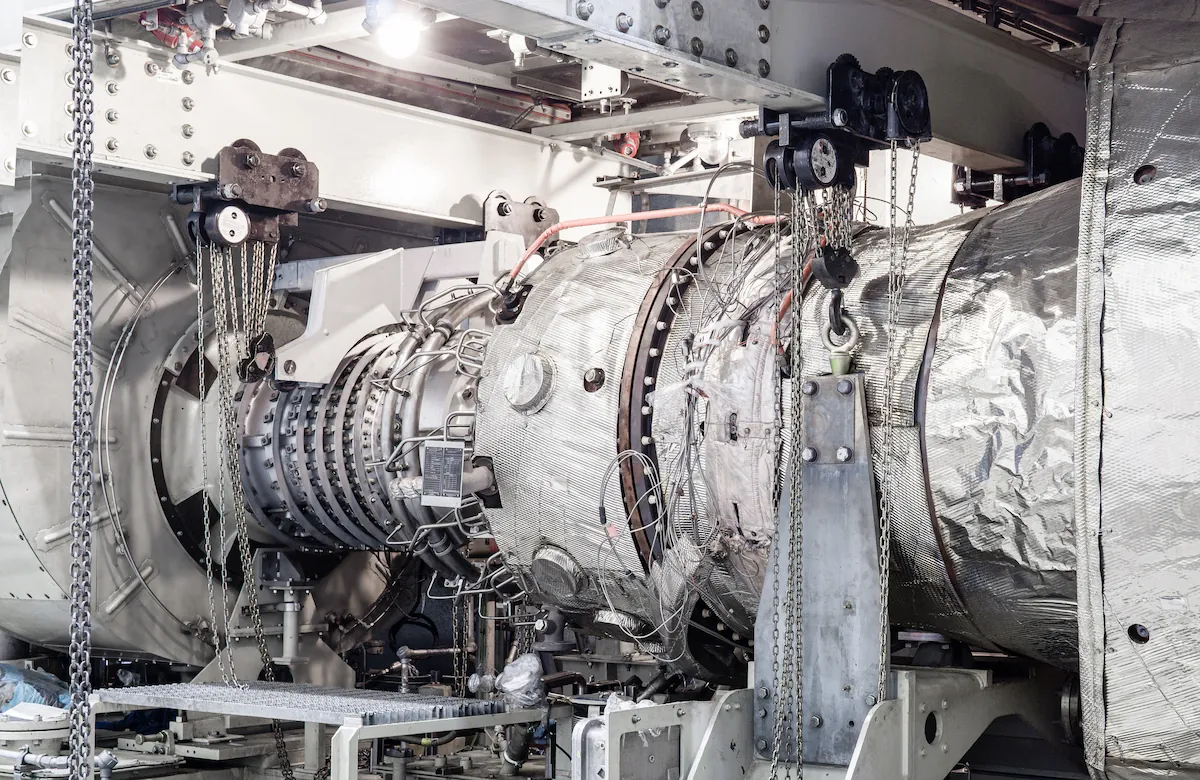
A steam turbine consists of several important components that work harmoniously and support performance efficiency, including:
- Blades: The blades, or propellers, on a steam turbine are designed to catch energy from the steam efficiently. Each blade is designed to regulate the direction, pressure, and speed of the steam.
- Rotor: The part of the turbine connected to the blades that turns the generator. The rotor is divided into a shaft rotor and a blade rotor. The shaft rotor functions as a place to install discs, while the blade rotor functions as a tool to receive force from mechanical energy.
- Casing: A cover on the turbine that ensures its durability.
- Bearing: A bearing that functions to receive loads and support the shaft.
- Condenser: A machine for condensing steam into water for reuse in the boiler.
- Nozzle: A steam expansion medium for converting potential energy into mechanical energy.
- Seal: A seal installed around the shaft to prevent steam leakage.
Read also: Solar Power Plant: Definition, Benefits, and Example
Types of Steam Turbines
Steam turbines are classified into impulse, reaction, condensing, and non-condensing types. Here is the detailed explanation:
1. Impulse Turbine
Impulse turbines operate when extremely hot steam is channeled through turbine blades at high speed. As a result, the turbine can generate rotational motion and mechanical energy.
2. Reaction Turbine
Reaction turbines work by directing steam through fixed blades to the rotor blades. As a result, the turbine shaft rotates due to the change in the direction and speed of the steam.
The difference between reaction turbines and impulse turbines is that reaction turbines require more rows of blades to generate energy. Therefore, they are usually larger and heavier than impulse turbines.
3. Condensing Turbine
In a condensing turbine, steam is condensed at a pressure below atmospheric pressure to obtain maximum energy. This turbine aims to drive all the energy that can be obtained.
The process involved condensing steam into water for return to the boiler. Later, the heating process will be repeated. This type of turbine is more efficient than non-condensing turbines because it utilizes all of the steam condensation.
4. Non-Condensing Turbine
The steam leaves the turbine at a pressure above atmospheric and is used for heating or other processes before being returned to the boiler as water.
The difference between non-condensing and condensing turbines lies in the pressure at which they operate. Condensing turbines use high- and low-pressure stages to condense steam into water. Meanwhile, non-condensing turbines operate at a higher pressure than condensing turbines.
Applications of Steam Turbines
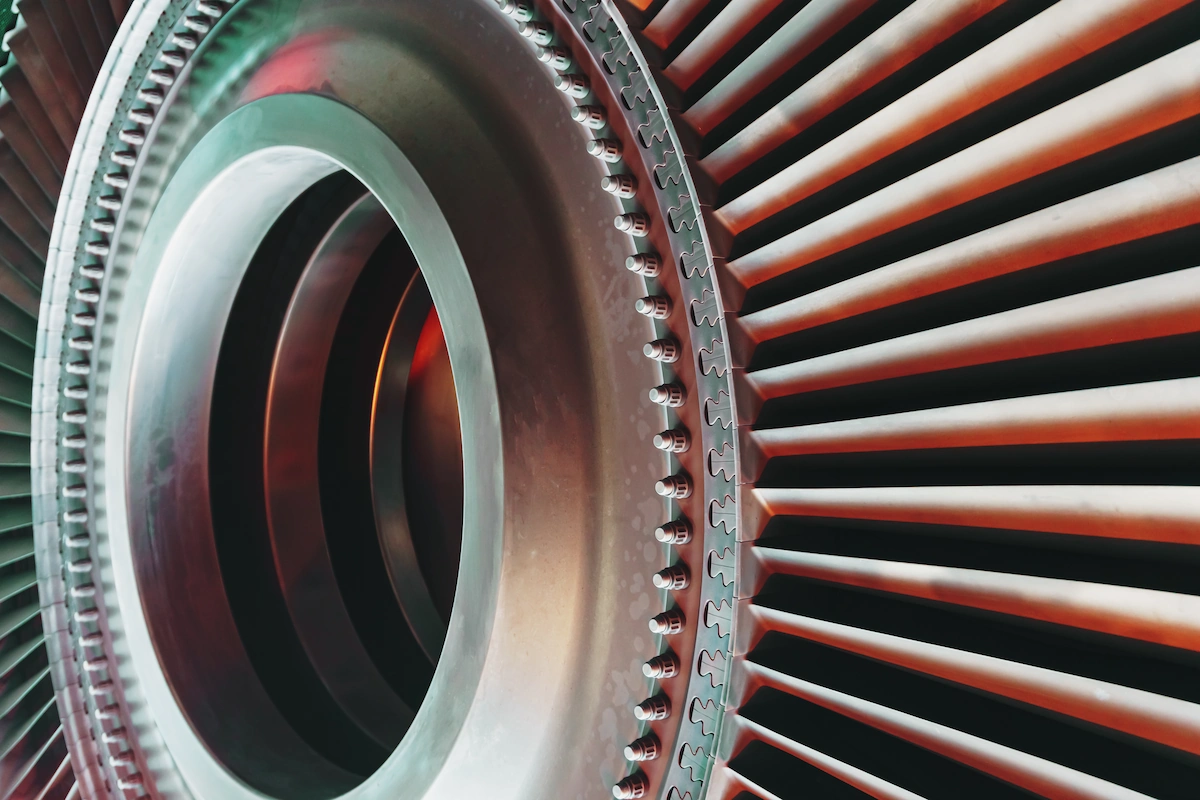
Steam turbines are widely used in industry, power plants, and ship engines. Some of their applications are as follows:
1. Ship Engines
Steam turbines are used to propel large ships across the oceans. The mechanical energy generated powers the ship's propellers.
The durability and efficiency of steam turbines in converting thermal energy into mechanical energy make them ideal for long voyages, ensuring ships have the power they need.
2. Industrial Processes
Several industrial processes, such as in petrochemical plants, use steam turbines to operate manufacturing facilities, including pumps and compressors. Steam turbines are versatile machines that can adapt to operational needs.
3. Power Plants
Steam turbines are widely used for power generation. In fact, these turbines can be considered the “backbone” of most power plants. The electrical energy generated by the generator is distributed to the power grid to light up cities and power factories.
Chandra Asri Group, Reliable Energy and Power Generation Solutions
Steam turbines are a vital component across various sectors, including power generation. Power plants are vital because they provide electricity to households, businesses, and manufacturing industries.
If you need electricity and renewable energy, trust Chandra Asri Group! Through Krakatau Chandra Energi, we provide a 120 MW power plant, serving 216 industrial customers and 1,609 household customers.
We operate a Combined Cycle Power Plant (PLTGU) consisting of two gas turbines, two HRSGs, and one steam turbine. Additionally, our power plant is supported by PT Krakatau Posco Energy, which operates a 200 MW coal-fired power plant.
We guarantee that the electricity we provide meets industry standards, is efficient, and reliable for your company's energy needs.
Do not let power outages disrupt your business operations! Contact Chandra Asri Group, #YourGrowthPartner, today!
Read also: Understanding a Gas Turbine, Mechanism, and Advantages
.png&w=3840&q=75)
.png&w=3840&q=75)