
28-01-2026
Understanding a Gas Turbine, Mechanism, and Advantages
A gas turbine is one of the technologies found in power plants. Generally, a gas turbine moves a generator, allowing it to produce electricity. Want to know more about how a gas turbine works? Read the complete information below!
What Is a Gas Turbine?
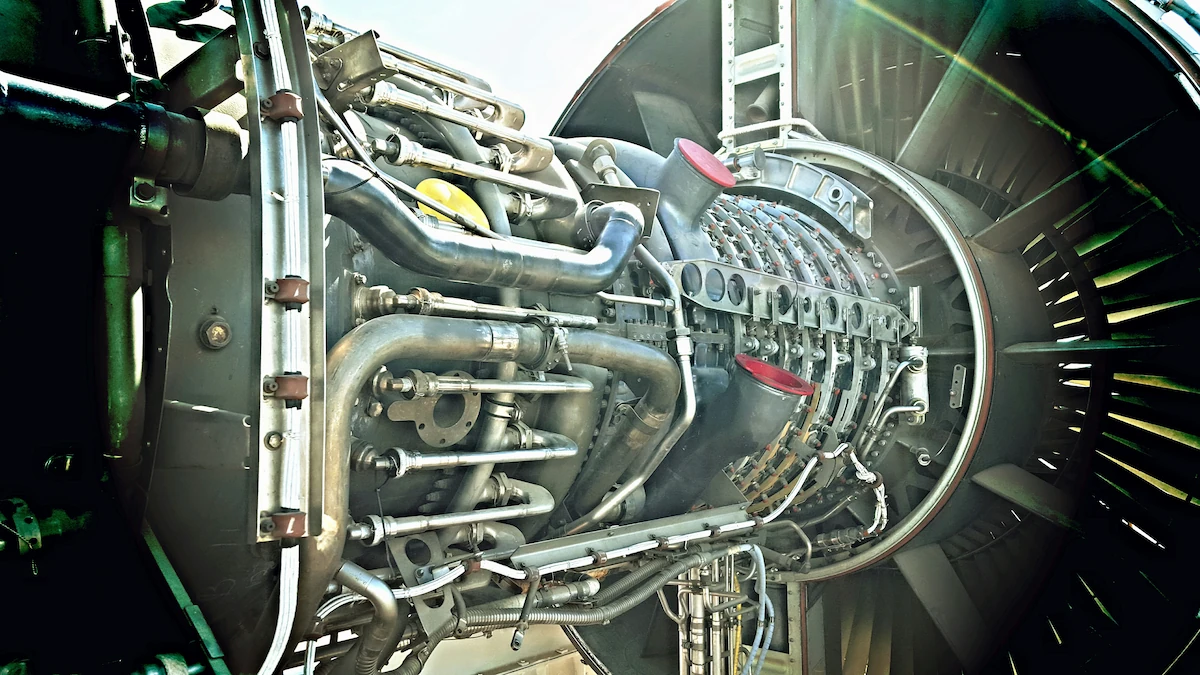
A gas turbine is a machine producing mechanical energy from natural gas. It is considered the “heart” of a power plant since the mechanical energy will rotate a generator. Then, the generator will produce electricity.
In addition to being in a power plant, you can find a gas turbine in an aircraft. Typically, a gas turbine implements the Brayton cycle involving natural gas combustion, air compression, and hot steam.
Moreover, a gas turbine is related to a steam turbine. That is why a power plant like a Combined Cycle Power Plant (CCPP) operates both turbines. The initial name of a gas turbine is derived from the operational process, which uses gas-formed air.
The main function of a gas turbine is to convert energy from fuels into another form of energy using controlled combustion. The heat resulting from this process will be used to boil water in the boiler, and the gas will be used to move a generator.
This turbine is considered more efficient, making it reliable for fulfilling the global energy demand. In fact, it applies the circular economy concept in the process, which involves the energy produced being leveraged for other industrial processes.
How a Gas Turbine Works
A gas turbine has a compressor, turbine, and combustion chamber. Here is how a gas turbine works:
- Air is taken from outside and compressed using a compressor. This increases the air pressure and temperature, making it easier to burn.
- The compressed air is mixed with natural gas in the combustion chamber and then ignited.
- The combustion process produces high-pressure hot gas that rapidly expands through the turbine blades.
- The turbine rotates, while the hot exhaust gas is expelled through the exhaust system. This residual heat can be used to heat water to create steam for other industrial processes.
- The turbine blades drive a generator to produce electricity.
Read also: 12 Types of Power Plants for Alternative & Renewable Energy
Types of Gas Turbines
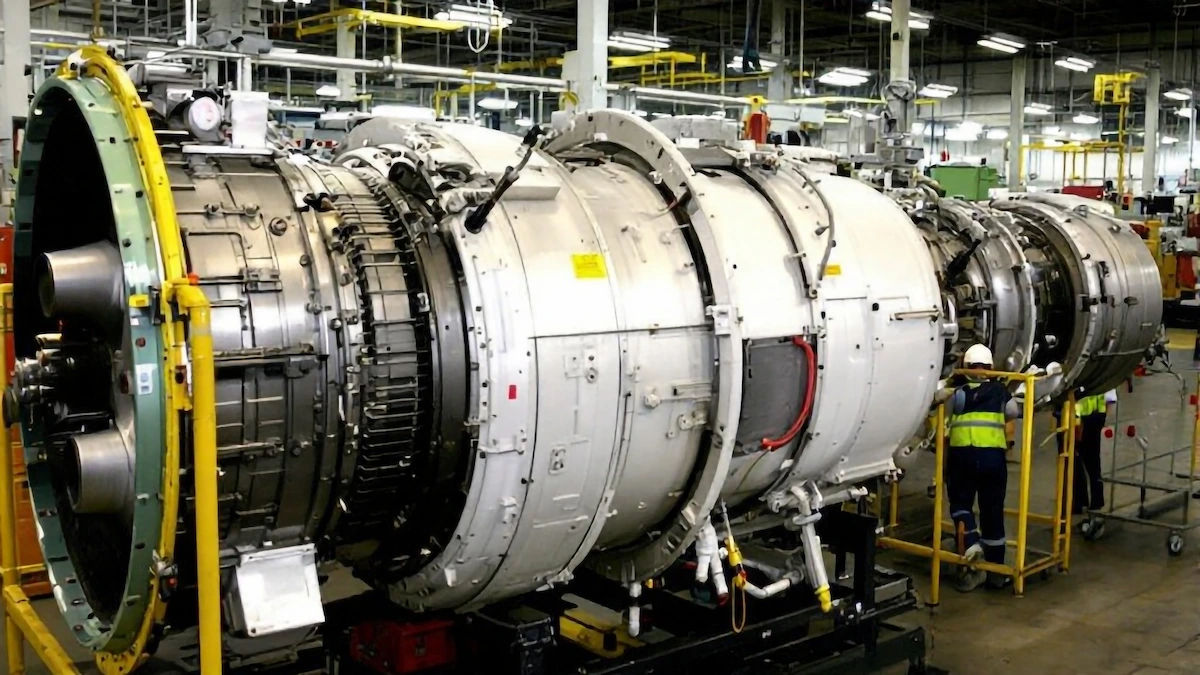

A turbine gas is widely used in various industries, such as aerospace and power plant industries. Here are some types of gas turbines you should know:
1. Closed Cycle Gas Turbine
Closed-cycle gas turbines use exhaust gas from the turbine to be compressed and reused in the same cycle. As a result, it is more environmentally friendly and efficient.
2. Open Cycle Gas Turbine (OCGT)
OCGT uses air compression mixed with natural gas, which is burnt in the combustion chamber. The hot gas from the combustion process will rotate the turbine, producing mechanical energy. Then, the residual gas will be released to the atmosphere. This type of gas turbine can be found in power plants.
3. Aero Gas Turbine
Aero gas turbines are used to provide great thrust to aircraft, but with high energy efficiency. Not only that, but the thrust created must also be resistant to extreme conditions during flight.
4. Combined Cycle Gas Turbines
A combined cycle gas turbine is used to optimize the energy efficiency. It captures heat residue to move the additional steam turbine, producing extra electricity. This type of turbine is used in the Combined Cycle Power Plant (CCPP).
Regarding CCPP, Chandra Asri Group, through Krakatau Chandra Energi, operates CCPP with a capacity of 120 MW. Our CCPP has two gas turbines, one steam turbine, and two HRSGs. By using natural gas, we guarantee that the energy quality meets the industrial standard.
5. Heavy Gas Turbine
This turbine is designed in a more durable and larger frame, allowing it to operate in high temperatures. This type of turbine can be found in the refinery.
6. Industrial Gas Turbine
The industrial gas turbine has a heavier construction, especially in the frames and propellers. Consequently, this turbine produces electricity and mechanical energy reliably for the industry.
7. Microturbines
Microturbines are a simple version of a gas turbine. This version is used in the refrigerators installed in hotels, offices, and hospitals.
Read also: Solar Power Plant: Definition, Benefits, and Example
Advantages of a Gas Turbine
Gas turbines are known for their high energy efficiency due to the cogeneration process. Cogeneration, or Combined Heat and Power (CHP), is the process of producing two types of energy at once: electrical energy and heat.
This process burns fuel (in this case, natural gas) to generate energy that drives the generator, while the heat energy produced is used to heat water or for other industrial processes.
In addition to their efficiency, gas turbines also have many other advantages, such as:
- They do not produce much waste heat because it is reused for other processes.
- They have a wide range of uses, such as for power plants, aircraft engines, ship engines, train engines, and industrial engines.
- They do not release many gas emissions into the atmosphere thanks to innovations in modern combustion technology.
- They can adapt to market demand.
That concludes the information about a gas turbine you can learn. This turbine is one of the crucial components in the power plant, allowing it to generate electricity.
If your company needs an electricity provider, Chandra Asri Group, as #YourGrowthPartner, and Krakatau Chandra Energi are ready to support it with the use of efficient and reliable energy infrastructure.
Contact us and get a reliable energy solution for your company!
Read also: 7 Examples of Electrical Energy and How to Generate It
.png&w=3840&q=75)
.png&w=3840&q=75)