
28-01-2026
Electrical Blackout: Causes, Effects, & How to Deal with It
A blackout is a widespread power outage that can occur at any time. Its impact is significant because prolonged outages can paralyze various activities. That is why power plants often become the solution to sustainable blackouts.
This article explains electrical blackouts and their impact. So, read on until the end!
What Is an Electrical Blackout?

An electrical blackout is a sudden, widespread power outage. One cause of electrical blackouts is an imbalance between electricity production and consumption.
Electrical blackouts can indicate that an electrical system has experienced a total failure. In Indonesia, blackouts generally occur due to disruptions in the transmission network, causing the protection system to cut off the electricity supply to prevent further damage.
So, how long can a power outage last? Two situations affect the duration of a blackout. If the network can be restored, for example, with support from other areas, electricity can return after 4-8 hours.
However, if extensive network repairs are needed, electricity may not be restored for 10 hours or more.
The problem is that electricity is one of the main sources of energy humans use. Its unavailability will certainly disrupt activities ranging from business and household to manufacturing.
A study published in the Journal of World Development found that an electrical blackout in Indonesia can reduce MSME employees' productivity, leading to losses of up to Rp71.5 billion per year for companies.
This indicates that the development and reliability of electricity supply in Indonesia are urgently needed to ensure that business processes, manufacturing, and households can operate smoothly.
One of the worst electrical blackouts in Indonesia occurred on August 18, 2005. At 9 a.m. Western Indonesian Time, Java, and Bali experienced a blackout due to damage to the 500 KV Saguling, Cilegon, and Cibinong Extra High Voltage Transmission Lines.
As a result, 50% of the electricity supply was lost. This blackout lasted for 24 hours, particularly across Java and Bali. However, in the Banten and Jakarta areas, the impact lasted only about 3 hours.
Read also: 12 Types of Power for Alternative & Renewable Energy
Causes of Electrical Blackouts
Power system blackouts can be caused by various factors, ranging from natural to technical. The most common causes of electrical blackouts are severe weather, such as tornadoes, snowstorms, and flash floods.
Total blackouts can also occur during extreme heat or cold weather. In addition to natural factors, blackouts can also occur due to technical factors, including:
- Overloading of the system: Electrical loads that exceed the system's capacity, such as increased demand, can cause protection system failures and overloads, leading to power outages.
- Damage to high-voltage overhead lines or submarine cables: It can cause total power outages, even across an entire island.
- Transmission network disruptions: This network is a crucial component of electricity distribution to consumers, so any disruption can increase the risk of blackouts.
Impact of Power Blackouts
Power blackouts can affect several sectors and the economy. During a total blackout, you may lose access to clean water, electricity, heating and cooling, information services, the internet, and communication channels.
Not only that, several businesses and public facilities will also be negatively affected, including grocery stores, minimarkets, ATMs, banks, gas stations, hospitals, and pharmacies.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) summarizes the relationship between economic impact and the duration of total blackouts in several countries.
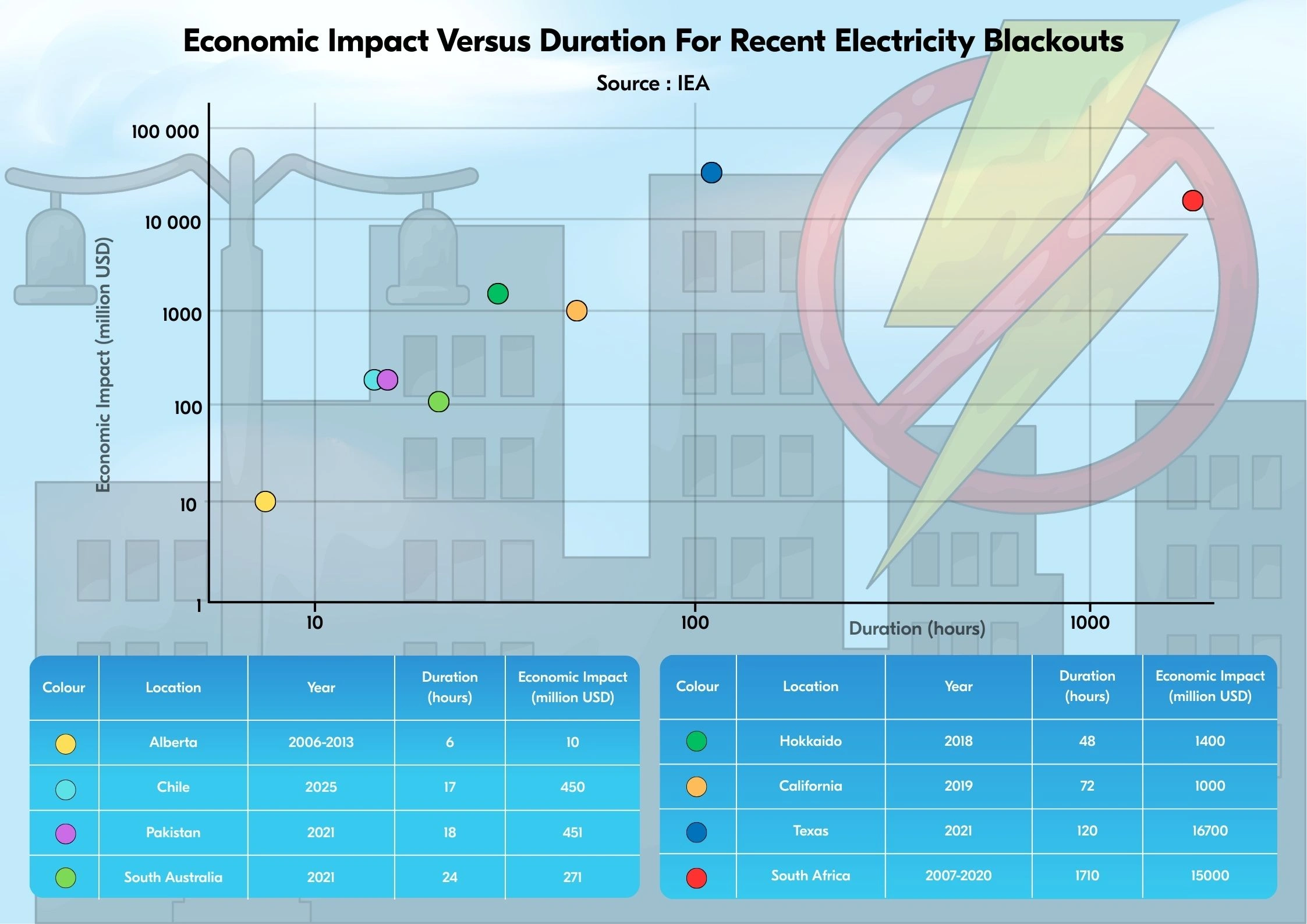
Based on the data, the total blackout in Chile in 2025, lasting 17 hours, caused economic losses of up to 450 million dollars. Then, in 2021, the Texas blackout had an economic impact of $ 16 billion, lasting 120 hours.
So, it can be concluded that the longer the duration of a power outage in an area, the greater the economic losses incurred.
Read also: Combined Cycle Power Plant (CCPP), How Does It Work?
Things to Do During an Electrical Blackout

When a power outage occurs, there are several things you need to do during and after the incident, including:
1. During the Incident
During the incident, you must determine whether only your location is experiencing a blackout. You can check the electrical panel in the building and communicate with your neighbors.
After that, you can contact the electricity provider's office to report the incident and the extent of the affected area. While waiting for a follow-up from the electricity provider's office, you can take the following safety measures:
- Turn off and unplug all electronic devices (except refrigerators).
- Lower the temperature on heaters or air conditioners to the minimum setting to prevent damage when power returns.
- Avoid using ovens or gas stoves as a source of heat to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Turn on one light switch inside the room and outside the building as a reference when the power comes back on.
- Avoid using generators, portable stoves, and charcoal briquettes indoors to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning or dangerous smoke.
- Close the refrigerator door and monitor its temperature during the outage.
- Store non-perishable food and water for activities.
- If the building or residence is uncomfortable to live in during a blackout (e.g., too hot, too cold, or flooded), immediately leave to find a safe place.
2. After the Incident
Once power is restored, wait 10–15 minutes before turning on all electronic devices to ensure that the power supply is stable. Then, you can start turning on essential appliances, such as lights, refrigerators, and heaters (if the weather is cold).
Next, check the food in the refrigerator to monitor its last temperature. If it is still cold, it means the refrigerator is still functioning. If a significant amount of food has spoiled, immediately discard it and contact a technician to repair the refrigerator.
The Difference Between a Blackout and a Brownout
The term blackout is often used interchangeably with brownout. However, the two have differences, especially in the affected area.
A brownout refers to a partial power outage. This usually occurs due to a drop in the power supply voltage. This outage can also be intentionally implemented to reduce electrical load in an emergency.
Meanwhile, a blackout is a total power outage, more severe than a brownout. When it occurs, almost all electrical activities are disrupted, thus having a wider impact.
Prepare a Backup Power Supply with Solar Panels
Brownouts and blackouts can occur at any time and unexpectedly. To be on the safe side, you can prepare an alternative energy source so that you are not completely dependent on electricity from burning fossil fuels.
In this regard, you can install solar panels in your house or building. Solar panels are now available in various systems, including on-grid, off-grid, and hybrid.
Chandra Asri Group and Krakatau Chandra Energi offer all three types of solar panels, so you can choose the one that best suits your company's needs.
On-grid solar panels do not require batteries, while off-grid panels do, to store energy when not in use. So, when a power outage occurs, you can use the electrical energy stored in the solar panel batteries.
Contact us now and entrust your energy needs to Chandra Asri Group, #YourGrowthPartner!
Read also: Solar Power Plant: Definition, Benefits, and Example
.png&w=3840&q=75)
.png&w=3840&q=75)