
28-11-2025
What Is a Petroleum Reservoir in the Oil and Gas Industry?
When we talk about refining crude oil, you might also have heard of a reservoir. Then, what is a reservoir? It is a hidden “well” under the Earth containing much crude oil.
As a result, the reservoir becomes a primary component of the oil and gas industry. This article discusses the role of the reservoir in the industry. So, read the complete information below.
What Is a Reservoir?
A reservoir is an underground “tank” that saves crude oil, natural gas, and groundwater. It comes from hydrocarbon accumulation and porous rocks absorbing oil and gas. Typically, a reservoir tank is located deep underground.
Yet, even though it absorbs many hydrocarbons, it does not mean it has the shape of a lake because it lacks a cavity. Rather than a lake, a reservoir is like a hydrocarbon deposit with layers.
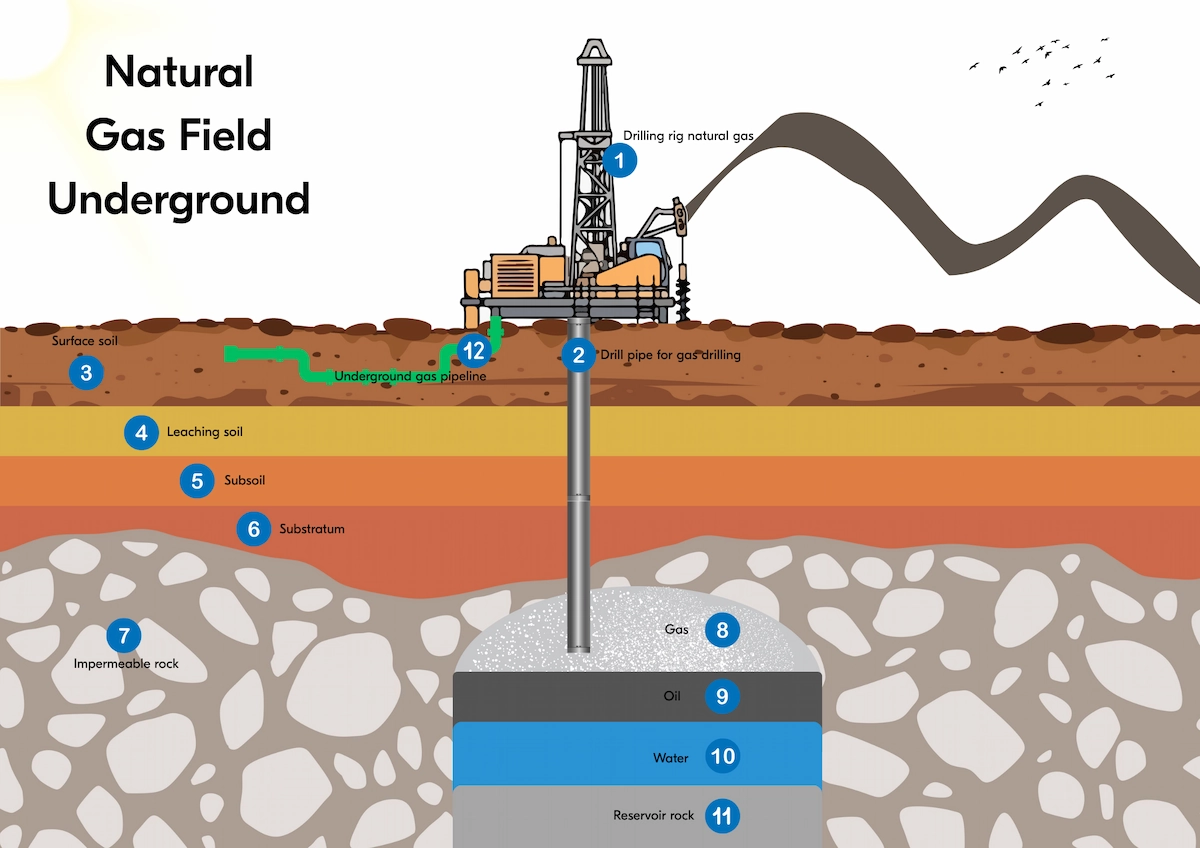
Thus, to obtain hydrocarbons, a company must drill into the ground. When they are lifted, they will be processed into consumer or industrial products.
The existence of a reservoir really affects the global energy needs. According to Statista, the global oil demand in 2024 reached 103.75 million barrels per day. In 2025, demand is forecast to reach 105 million barrels per day.
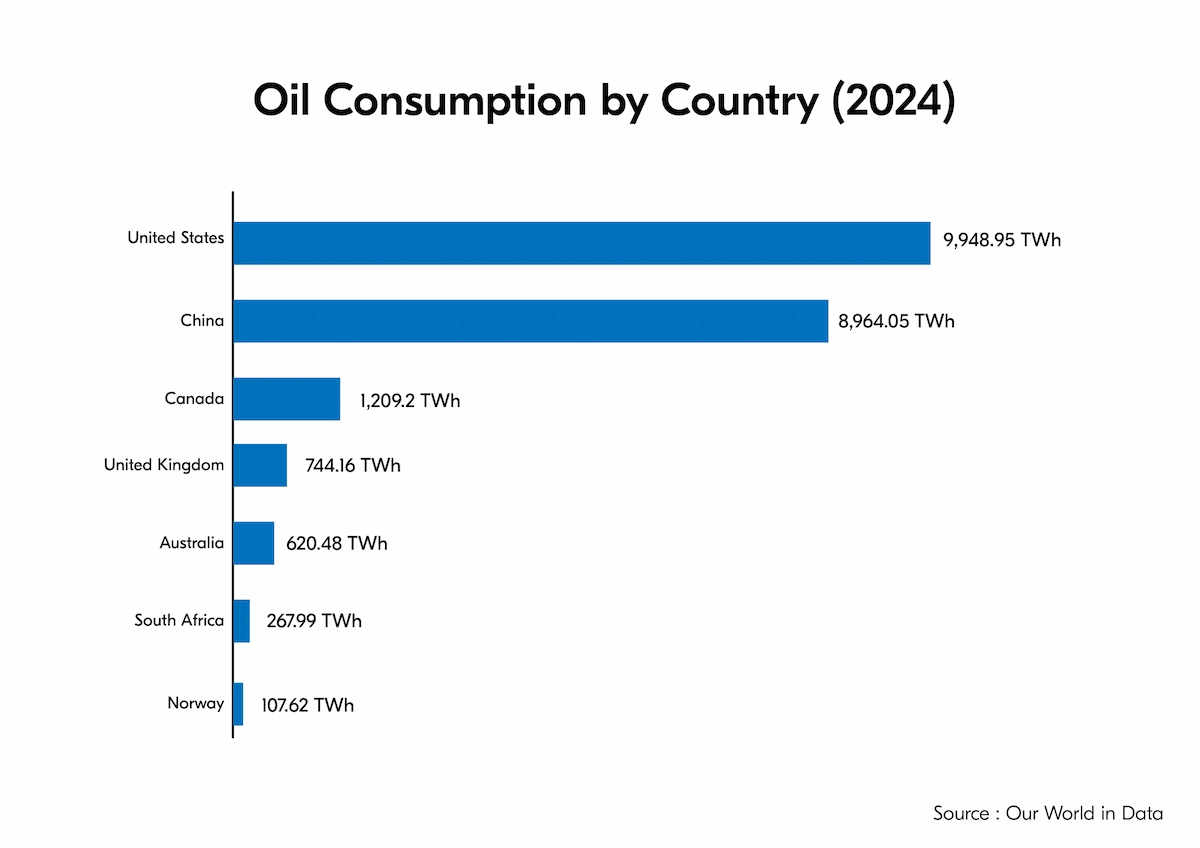
Moreover, Our World in Data reported that in 2024, the United States became the country with the most oil consumption, at 9,948.95 TWh, followed by China and Canada.
The Structure of a Hydrocarbon Reservoir

A reservoir contains several layers that allow oil, gas, and water to be deposited. Here are the main components of a reservoir:
- Rocks: A reservoir consists of porous stones in various sizes. These rocks create a path for hydrocarbon movement. The solid rocks protecting the path are called matrixes.
- Reservoir fluids: Not only rocks, but reservoirs also contain water, which accompanies the hydrocarbons.
- Cap layer: This impermeable layer is located at the edge or top of the reservoir.
In addition to these three components, conventional hydrocarbon reservoirs typically include source rock, reservoir rock, and cap rock.
Source rocks are formed from crude oil and natural gas’s kerogen. Reservoir rocks are porous and impermeable rocks that absorb oil and natural gas.
Cap rocks are layers of rock that cover the top and edges of reservoirs. Here, water also covers the bottom of the reservoir.
Read also: Natural Gas Compositions, Its Types, and Its Advantages
Reservoir Formation Process

Initially, dead plants and animals were buried for over a million years. During this period, a layer of sand, mud, and sediment was formed. After that, the fossils were exposed to high pressure and heat, turning into petroleum and gas.
For a reservoir to form, natural gas and oil must move from the source rock to the reservoir rock. This process typically occurs over millions of years.
The oil and gas could move to the reservoir rocks because they had a lighter density than water. Then the reservoir rocks would trap the hydrocarbons (oil and gas).
Reservoir rocks are also the area that will be drilled during the extraction process. Because they are formed from porous rocks of varying sizes, gaps form between them. These gaps allow groundwater to pass through.
To access the hydrocarbons trapped in the reservoir rocks, you need to drill into them. The pressure difference between the reservoir and Earth's surface pushes the hydrocarbons to the surface.
After that, the hydrocarbons are extracted and sent to oil and natural gas processing plants. Here, the hydrocarbons are separated, cleaned, and processed into industrial raw materials or consumer products.
Read also: Oil Refinery: Definition, Processes, and Its Functions
The Characteristics of a Reservoir

Experts must understand the characteristics of a reservoir. That way, they can use the proper and effective strategies. Below are several characteristics of a reservoir you must know:
1. Porosity
Porosity is the number of pores in the rock formations. It is one of the most essential parameters because, typically, high-porosity rocks hold more hydrocarbons than low-porosity rocks.
2. Relative Permeability
Relative permeability measures the amount of gas or water that flows relative to the other phase. This property shows how effective permeability is for each fluid phase.
3. Permeability
Permeability measures how easily fluids, such as oil, gas, and water, flow through porous rocks. It is affected by pores or gaps in the rock formation and by rock size.
4. Saturation
Saturation determines the portion of the porous space occupied by the fluid in the fluid-binding rock formation. Saturation is essential for evaluating the reservoir potential.
5. Hydraulic Fracture Pressure
Hydraulic fracturing pressure is the pressure required to initiate fractures in a rock formation. This technique is used to extract hydrocarbons from unconventional reservoirs. The method involves injecting high-pressure fluid into the reservoir and rock fractures to create channels for hydrocarbon flow.
6. Natural Fracture
A natural fracture is created by geothermal pressure or tectonic movement. This fracture can affect the hydrocarbon and water flow. Also, it is crucial for hydrocarbon extraction.
7. Pressure Difference
Pressure difference measures the contrast between two points in the reservoir. This data can help experts understand the hydrocarbon flow and determine the right extraction strategy.
8. Reservoir Pressure
Reservoir pressure determines the pressure within geological formations containing hydrocarbons. Rock formations, rock porosity levels, and other factors can influence reservoir pressure.
This concludes the information on reservoirs and the characteristics to be considered. Reservoirs are a key factor in oil and natural gas production. After extraction, oil and natural gas are used to produce several chemicals.
Regarding chemicals, Chandra Asri Group provides chemical solutions with the highest quality raw materials. We are one of the largest integrated petrochemical producers in Indonesia, supplying raw materials for plastics, vehicle tires, caustic soda, and other industrial products.
Meet your industrial chemical raw material needs with chemical solutions from Chandra Asri Group!
Read also: Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Characteristics and the Reactions
.png&w=3840&q=75)
.png&w=3840&q=75)